The staggering speed of change and the increasing complexity of information-based services, whether for business, entertainment, healthcare, government or other industries, continues to push infrastructure densification. Digital transformation, at least in the data center, must deliver reliable, scalable networks to meet these demands. Robust fiber network management has become crucial for today’s organizations, and their customers, to ensure continuous highspeed data transport and end-to-end delivery of services.
Data center build and use costs are rising and, as a result, data center owners are looking to maximize the compute, network and storage resources across smaller physical footprints. This in turn, drives the need for a higher density physical infrastructure and improved resource utilization while also offering increased workload mobility.
Another trend that is applying pressure for higher densities comes from the increasingly dynamic hyperscalers provisioning space within locally situated multi-tenant data centers (MTDCs) as part of their Edge strategy to provide a more local (lower latency) presence for their customers. In order to improve ROI, these MTDCs are focused on optimizing their space utilization in both the white space and grey space.
The market growth in digital devices and communication continues unabated. The global Cloud Computing Market size was valued at $545.8 billion in 2022 and it is projected to reach $1,240.9 billion by the end of 2027, growing at a CAGR of 17.9 percent.
To meet this demand, the uptake of higher data rates has accelerated from 40 gigabits to 400 gigabits, with 800 gigabit devices available, and the roadmap to 1.6 terabytes clearly planned. With each increase in data rate, the density of compute power per square meter increases, but also puts even more focus on having a reliable high density physical infrastructure.
As an example of the speed of data center development, Panduit is currently supporting a top five hyperscaler across EMEA to deploy high-performance cabling infrastructure within MTDCs at a rate of one site per nine days.
All of these builds utilize the maximum fiber density components such as enclosures (144 fibers per RU), 2mm diameter Uniboot duplex LC fiber patch cords and the smallest diameter rollable ribbon trunk cabling available (12.5mm for 288 fibers and 17mm for 576 fibers).
The smaller diameter fiber cabling enables the higher densities in the pathways and racks while also relieving congestion at the panels to make it less likely for adjacent fibers to be disturbed during Moves, Adds, or Changes (MAC). The end result is a data center that meets the requirements for efficient space utilization.
Crucial to these and similar installations, are optical distribution frames (ODF) which are generally the areas of highest density fiber connections. These frames provide a passive environment to distribute and manage all of the fiber cabling coming into a data center and are, therefore, normally access controlled. Selecting the right ODF will maximize flexibility, manageability, security and scalability.
Versatility is key
The latest ODF solutions provide modular building blocks that can be assembled to create the exact frame and cable manager configuration to optimize density and system availability. Typical frame arrangements are wall mounted single or double racks, and middle of the room back-to-back configurations.
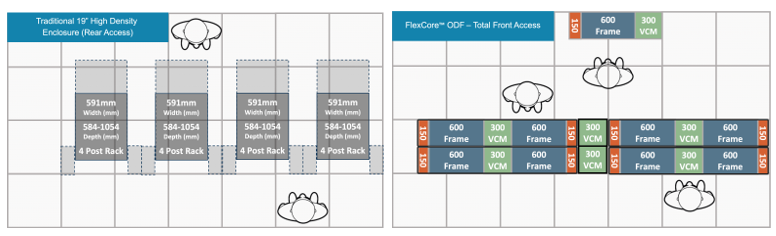
Modular systems offer flexibility and reduce floor space by as much as 50 percent compared to standard four post racks. For a MTDC, this reduction in floorspace requirements effectively increases the operational rental floorspace which has a significant positive impact on the site’s overall income and profitability.
In diagram three below, four traditional racks with 19” high density enclosures offer a capacity of 23,040 fibers and occupy 12 floor tiles. As an example, the Panduit ODF front access solution features a compact frame system that can be placed back-to-back to achieve the same 23,040 fiber capacity, but within a floor space requirement of only 6.5 tiles.
These innovative modular platforms are designed for data centers that require network patching in the white space and Meet-Me Rooms (MMR). The ODFs also work well in smaller areas, as the front access frames are designed for wall mounting. Therefore, previously non-revenue earning areas can now be utilized, ensuring customers receive the most efficient and effective cabling infrastructure layout.
A high density ODF also enables data center operators to meet their growing demands for new services, simplify day-to day MACs and futureproof their investment.
MACs and security
Managed network connectivity is essential and ensuring MACs are processed correctly and recorded is vital to the operational efficiency of the IT space, whether whitespace or grey space. Intuitive cable management and easy access to the fiber connectivity in a high density ODF can increases the ease of use and speed of MACs by up to 40 percent.
In addition, utilizing the newest fiber connectivity with boots that can be used as pull tabs and small diameter cable greatly reduces the risk to adjacent circuits during the MACs.
In the latest (2022), ITIC Hourly Cost of Downtime survey, human error (64 percent) is second to security breaches (73 percent) as the key issue that most negatively impacts reliability and causes downtime. Systems, like a properly designed ODF, can reduce or eliminate human error which improves customer satisfaction and overall profitability.
There are various digital, and paper-based systems for recording new installs and MACs, but it is vital that it is done rigorously and dynamically, so that the network information is accurate, and changes recorded. As cabling infrastructure becomes denser and more complex, the need to record and manage cable runs is migrating to digital formats, essential to the reduction in human error incidents.
It is important to choose an ODF that offers clearly defined and traceable cable routing pathways that reduce guesswork and help limit the need for rip and replacing cabling. Multiple-level lockable security on the ODF at both the door and enclosure is important to MTDCs for reducing accidental human error and adding compartmental security between multiple tenants.
Conclusion
The continued drive to shrink all aspects of the data center is being realized through the expansion of higher data rate electronics. To take advantage of this, high-density, high-performance fiber infrastructure is increasingly important.
Innovative designs are now offering cost effective solutions that are futureproofed and can scale as needed to defer CAPEX spending. High Density ODFs offer well engineered, expandable configurations with the capability of hosting the highest fiber counts in a highly organized simple to use format. They also offer security in areas where human error is often the cause of costly and preventable downtime.
Choosing an ODF that meets all of these requirements and is globally available is an important step for hyperscalers and MTDCs to standardize on a design that optimizes density and simplifies installation.
For more information, visit www.panduit.com/ODF
More from Panduit
-

Sponsored Sustainability: Time to get your own blue flag
Waving the blue flag for a greener future
-

Sponsored Powering 5G in building networks safely
Delivering power – and data – efficiently, safely, and securely
-

Sponsored Optimizing data center fiber infrastructure
Robust, flexible, integrated and sustainable – the fiber infrastructure needed to support today’s data center demands