We live in an increasingly data driven world. Individuals are consuming massive amounts of data at unprecedented rates, with the expectation that it be accessible anytime, anywhere. At the same time consumers are also generating a lot of data indicating their preferences, from what they want, to when they want it - and a variety of companies, ranging from financial firms to advertising agencies, find immense value in making sense of that data. Both the increased pace of information generation and the growing demand to process it quickly has resulted in many IT and IS managers looking for ways to make their data centers ready for the challenge.
Today’s data center architects and IT managers are feeling pressure to expand existing server infrastructures to enable faster processing of larger data sets. To make matters even more challenging, they are increasingly being asked to increase productivity with shrinking operating budgets. Simply adding additional servers is expensive and doesn’t solve the inherent server underutilization problem. That being said, IT professionals can turn to new technologies and scalable architectures capable of increasing performance while lowering overall system cost.
Hardware offloads
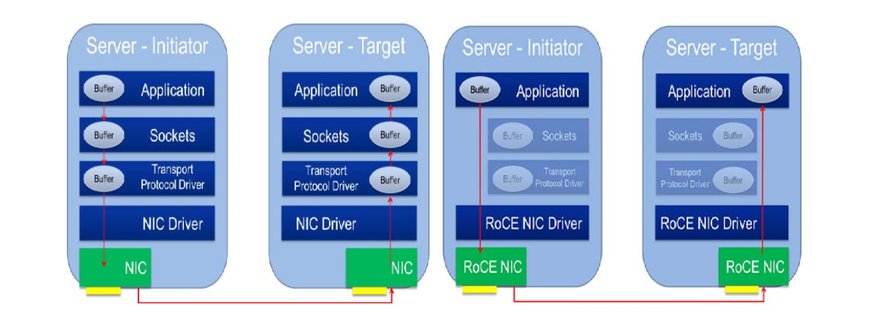
One such technology, Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA), is a remote memory management capability that utilizes hardware offloads to move data faster between servers with much less CPU overhead. Offloading the I/O from the CPU makes both data movement and the execution of applications more efficient. It delivers performance and efficiency gains that are not available from any other communications protocol including: low latency, improved resource utilization, flexible resource allocation, scalability and fabric unification.
RDMA first became widely adopted in the supercomputing space with InfiniBand but has expanded into enterprise markets and is now being widely adopted over Ethernet networks. RDMA over Converged Ethernet or RoCE (pronounced “rocky”) is driving an advanced data center architecture that eliminates dedicated storage area networks and converges compute, networking and storage traffic onto a single fabric. Leveraging the latest advances in reliable Ethernet and Data Center Bridging (DCB), efficient RDMA mechanisms in RoCE provide lower CPU overhead and increase mainstream data center application performance over Layer 2 and Layer 3 fabrics at all of today’s Ethernet speeds and beyond.
Data center architects running RDMA applications on an Ethernet infrastructure can expect to see application performance and efficiency improvements that come from the offloading of data movement and the higher availability of CPU resources to the application. Higher server productivity reduces the need for additional servers creating cost and power savings. RDMA also accelerates storage protocols such as iSCSI, SMB, and NFS making data movement across the datacenter more efficient as well. Furthermore, we are seeing RoCE deliver lower times for VM Migration in virtualized environments, higher performance data base workloads, and as a platform for improved application performance as Enterprise applications become more ‘HPC like.’
The RoCE specification is developed and maintained by the InfiniBand Trade Association (IBTA), and the IBTA promotes a healthy ecosystem by holding bi-annual RoCE plugfests. The IBTA also created the RoCE Initiative in June 2015 to highlight the technology’s many benefits and facilitate its adoption in enterprise data centers. Through this online resource, the RoCE Initiative:
- Enables CIOs, enterprise data center architects and solutions engineers to learn about improved application performance and data center productivity through training webinars, whitepapers and educational programs.
- Encourages the adoption and development of RoCE applications with case studies and solution briefs.
- Continues the development of specifications, benchmarking performance improvements and technical resources for current/future RoCE adopters
Interested in how RoCE can improve your data center? Find more here.
Brandon Hoff serves as the co-chair of the IBTA Marketing Work Group. He can be contacted at [email protected]