After years of offering virtual, anonymous cloud resources, Amazon is now offering users the ability to run their software on specific servers.
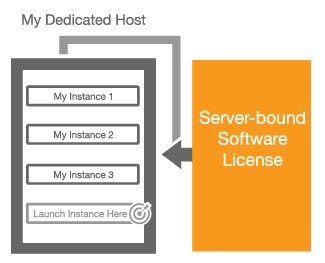
The new Dedicated Hosts feature in Amazon’s EC2 elastic cloud service lets users bring their own software licenses and access specific servers. The idea is to provide machines which are proof against “noisy neighbors” where a fellow customer hogs a particular resource, and to satisfy customers whos terms of operation require them to “own” their servers.
Dedication required?
The ultimate anonymity of the computing cloud is often not an appropriate way for a business to make use of cloud computing power. In many cases, an application for a specific business need requires dedicated computing power and a way to monitor and control a specific server, a need that has often been filled by data center vendors offering dedicated hosting. These needs range from specific computing power to requirements related to access to meet regulatory compliance.
With the new AWS EC2 Dedicated Host feature Amazon’s cloud services has moved to fill that niche, as well. Announced by Jeff Barr in the AWS official blog on Monday, the EC2 dedicated Hosts feature allows customers to bring their own server licenses for Windows Server, SQL Server, SUSE Linux Enterprise Server, as well as other enterprise systems and products to the cloud.
Users can make use of AWS Config to match server licenses to their dedicated hosts, with fine grained control via the Control Instance Placement feature over sockets and cores to make that license matching possible.
Users are still deploying virtual machines; this is not the bare metal install that a dedicated server in a colo facility provides, but it addresses licensing and compliance issues that previously were not possible to monitor with AWS and would have required a different solution. Customers are not getting dedicated hardware, but they can now deploy using AWS in both its shared and dedicated services modes. They can monitor all of their operations from within the AWS management interface as opposed to deploying different services on different providers.